NCERT Solutions Of CH 2 Acid Bases and Salts Class 10
NCERT Exercises are one of the most important parts of class 10 students as these questions are from the examination point of view for CBSE Board exams. Here at SidClasses we provide you with one of the best NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acid Bases and Salts that you can consider for your notes for the board exam.
Acids, bases, and salts are fundamental topics in chemistry, and it is very important for the students of class 10. Acids are substances that release H+ ions in their aqueous solutions, bases are substances that release OH- ions, in their aqueous solutions and salts are compounds formed by the reaction of acids and bases.
The strength of an acid or base is measured by its pH value. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 being acidic, and values above 7 being basic. The reactions between acids and bases are called neutralization reactions, and they form water and salt. The properties of acids and bases, as well as their reactions, have significant applications in various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and industry.
Jump To
Acid Bases And Salts Class 10 Solutions
Question 1
A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Solution: Option (d) 10
Question 2
A solution reacts with crushed-egg shells to give a gas that turns lime water milky. The solution contains
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KCl
Solution: Option (b) HCl
Question 3
10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralized by 8 mL of a given solution of HC1. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HC1 solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralize it will be
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL
Solution: Option (d) 16 ml
Question 4
Which one of the following types of medicines are used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic
Solution: Option (c) Antacid
Question 5
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filing
Solution:
(a) Zinc + dilute sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
(b) Magnesium ribbon + dil. Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
Mg (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
(c) Aluminium powder + dil. Sulphuric acid > Aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen
2Al (s) + 3H2SO4 (aq) → Al2 (SO4)3 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
(d) Iron filings + Dilute hydrochloric acid > Ferric chloride + Hydrogen
2Fe (s) + 6HCl (aq) → 2FeCl3 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
Question 6
Compounds such as alcohol and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Solution: Compounds like alcohol and glucose also contain hydrogen but they don’t release H+ ions in their aqueous solutions, so they are not considered acids. We can also prove this by showing that they do not conduct electricity.
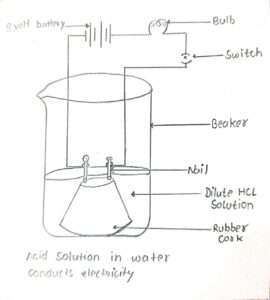
(i) Take a beaker with solutions of alcohol and glucose.
(ii) Fix two nails on a cork, and place the cork in the beaker.
(iii) Connect the nails to the two terminals of a 9-volt battery through a bulb and a switch, as shown in the given Figure.
(iv) Now pour alcohol into the beaker and switch on the current.
(v) we will observe that the bulb does not glow.
(vi) Repeat the experiment with glucose. There also the bulb will not glow.
(vii) This means H+ ions or any other ions are present in the solution.
This shows that alcohols and glucose are not acids.
Question 7
Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Solution: Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it doesn’t contain any ionic compounds like acids, bases, or salt dissolved in it. whereas rainwater conducts electricity because when it falls towards the earth’s surface it gets mixed with the atmospheric carbon dioxide and forms carbonic acid (H2CO3). This acid provides H+ ions and carbonate ions to rainwater.
Question 8
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Solution: As we know acids release H+ ions in their aqueous solution but in the absence of water it is not able to release H+ ions and hence do not show acidic behaviour in absence of water.
Question 9
Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is
(a) Neutral
(b) Strongly alkaline
(c) Strongly acidic
(d) Weakly acidic
(e) Weakly alkaline
Solution: (a) D
(b) C
(c) B
(d) A
(e) E
11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1 (in increasing the order by hydrogen ion concentration)
i. e., C < E < D < A < B
Question 10
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Solution: As we know hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a strong acid whereas acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid. So testube A containing HCl will release more H+ ions in comparison to testube B as a result of which Fizzing will occur more vigorously in test tube A.
Question 11
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer
Solution: Formation of lactic acid results in the making of curd from milk so the pH will fall below 6 in this case.
Question 12
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Solution:
(a) Milkman adds a small amount of baking soda to fresh milk to make it alkaline due to which, it does not easily gets sour or form lactic acid or converts into curd.
(b) The alkaline milk takes a long time to set into curd because the lactic acid being formed has to first neutralise the alkali present in it.
Question 13
Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Solution: The plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container because the moisture causes the slow setting of the plaster of Paris by bringing about its hydration which will make it hard and of no use after some time.
Question 14
What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Solution: It is the reaction in which acids and bases react together to form salt and water as products.
For example: NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Question 15
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Solution:
Uses of washing soda :
(i) Washing soda is used in the glass, soap and paper industries.
(ii) It is used for removing the permanent hardness of the water.
Uses of baking soda :
(i) Baking soda is used as an antacid in medicines to remove the acidity of the stomach.
(ii) Baking soda is used for making baking powder (used in making cakes, bread, etc.).
We hope that the class 10 science chapter 2 Acid Bases and Salts question answer helped you a lot to make your notes. If you have any queries regarding the class 10 science chapter 2 question answer, please let us know in the comment section. We will try to answer you as soon as possible.